Coffee Roasting Glasses based on M5Stack AtomS3(Part2)
-
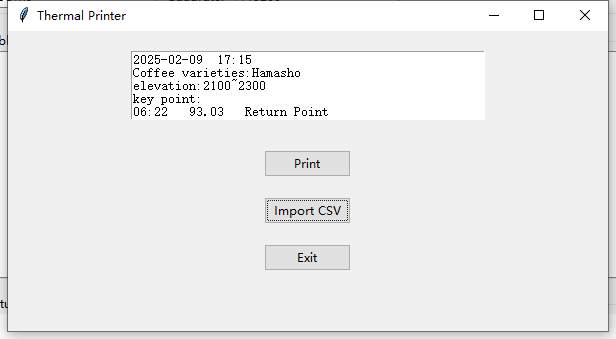
(3) Background Monitoring and Printing Program: Using the Python language, a monitoring and printing program for coffee bean temperature during roasting was written for Windows. Besides monitoring the bean temperature in real-time, it can also mark key points (e.g., Turning Point/Turnaround, First Crack, Drop Point), add simple notes, and finally print a record label of the roasting parameters via a serial thermal printer. This label is stuck onto the container of the roasted beans, completing a full coffee roasting and data recording session.

Step 1: Thermal Printer Part: The TTL level interface of the 58mm thermal printer is connected to the PC via a USB-TTL converter module.
Step 2: Temperature Data Acquisition: AtomS3 --> PC via USB. The temperature data is sent in a dual transmission mode: sent to the glasses via ESP-NOW and sent to the PC via USB (serial).
Step 3: PC GUI design and code.
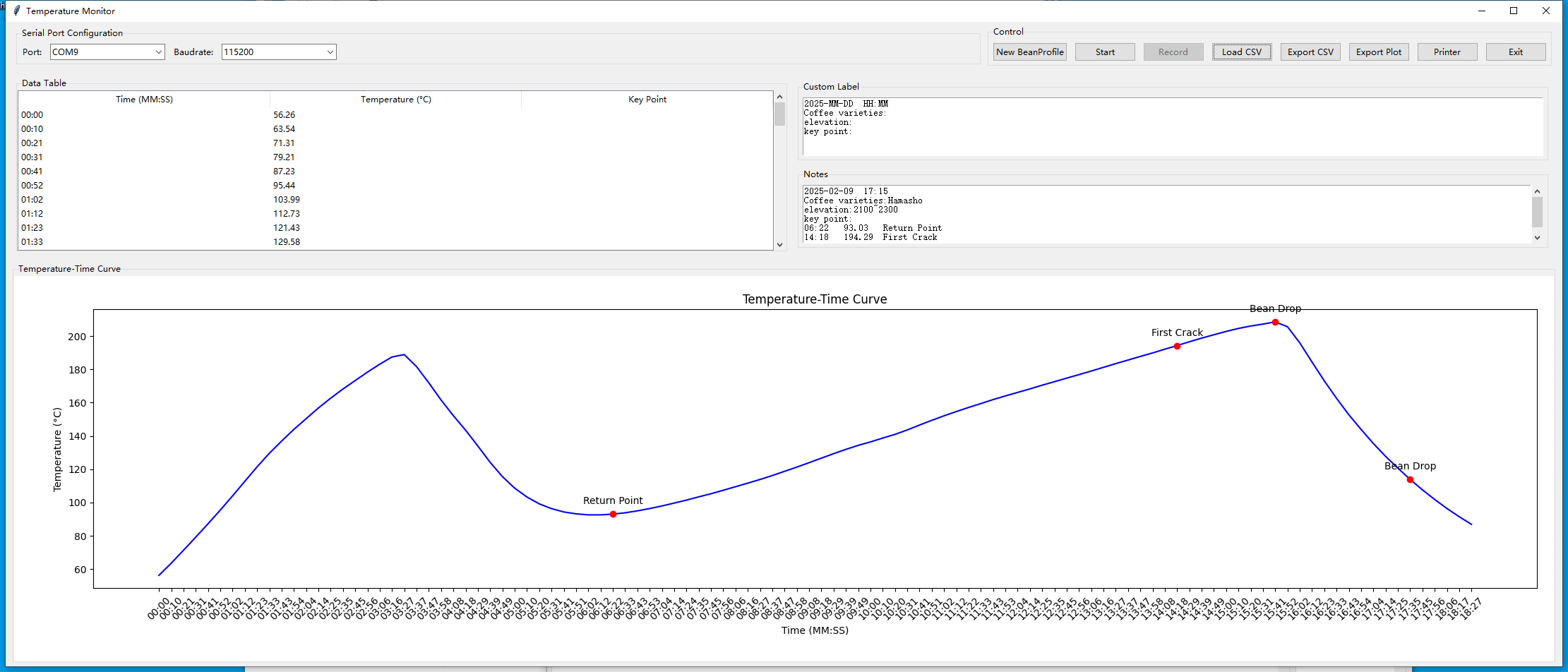
(4) Semi-Direct Flame Gas Roaster: This is not made by me. It is used for roasting green coffee beans. Our coffee roasting glasses, used with this roaster, allow for roasting 100g batches of coffee beans at home, enjoying the fun of DIY coffee beans.

Code:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk, scrolledtext, messagebox, filedialog import serial import serial.tools.list_ports import threading import time import csv import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg from datetime import datetime from Adafruit_Thermal import Adafruit_Thermal from tkinter import Toplevel import os from PIL import Image # 全局变量 is_running = False is_recording = False serial_port = None data = [] last_data_time = 0 fig, ax = None, None canvas = None #添加打印窗口类: class PrinterApp: def __init__(self, master): self.window = tk.Toplevel(master) self.window.title("Thermal Printer") self.window.geometry("600x300") self.printer_initialized = False self.printer = None self.label = tk.Text(self.window, width=50, height=5, wrap=tk.WORD) self.label.pack(pady=20) self.print_button = ttk.Button(self.window, text="Print", command=self.print_text) self.print_button.pack(pady=10) self.import_button = ttk.Button(self.window, text="Import CSV", command=self.import_csv) self.import_button.pack(pady=10) self.exit_button = ttk.Button(self.window, text="Exit", command=self.exit_app) self.exit_button.pack(pady=10) # Initialize printer self.init_printer() def init_printer(self): """ Initialize the thermal printer """ # 如果之前的打印机对象存在,先尝试关闭它 if self.printer is not None: try: self.printer.close() except: pass # 忽略关闭时的错误 try: # Modify the COM port according to your connection, use COMx on Windows, /dev/ttyUSBx on Linux self.printer = Adafruit_Thermal("COM8", 9600, timeout=5) self.printer.setDefault() self.printer_initialized = True messagebox.showinfo("Success", "Printer initialized successfully") except Exception as e: self.printer_initialized = False self.printer = None messagebox.showerror("Printer Error", f"Failed to initialize printer: {e}") def print_image(self, image_path): if not self.printer_initialized: messagebox.showerror("Printer Error", "Printer is not initialized") return try: image = Image.open(image_path) if image.mode != '1': image = image.convert('1') width = image.size[0] height = image.size[1] if width > 384: width = 384 rowBytes = (width + 7) // 8 bitmap = bytearray(rowBytes * height) pixels = image.load() for y in range(height): n = y * rowBytes x = 0 for b in range(rowBytes): sum = 0 bit = 128 while bit > 0: if x >= width: break if pixels[x, y] == 0: sum |= bit x += 1 bit >>= 1 bitmap[n + b] = sum self.printer.printBitmap(width, height, bitmap) self.printer.feed(1) except Exception as e: messagebox.showerror("Printer Error", f"Failed to print image: {e}") def print_text(self): if not self.printer_initialized: messagebox.showerror("Printer Error", "Printer is not initialized") return image_path = r"D:\Documents\deepseek\ffcoffee2.bmp" if os.path.exists(image_path): self.print_image(image_path) else: messagebox.showwarning("Warning", f"Image file not found: {image_path}") text_to_print = self.label.get("1.0", tk.END).strip() if text_to_print: try: self.printer.println(text_to_print) self.printer.feed(2) messagebox.showinfo("Success", "Image and text printed successfully") except Exception as e: messagebox.showerror("Printer Error", f"Failed to print text: {e}") else: messagebox.showwarning("Input Error", "Please enter some text to print.") def import_csv(self): file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=[("CSV files", "*.csv")]) if file_path: try: with open(file_path, newline='', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile: reader = csv.reader(csvfile) rows = list(reader) for i, row in enumerate(rows): if 'Notes' in row: notes_index = row.index('Notes') if i + 1 < len(rows): notes_value = rows[i + 1][notes_index] self.label.delete("1.0", tk.END) self.label.insert("1.0", notes_value) return messagebox.showwarning("CSV Error", "No 'Notes' column found in the CSV file.") except Exception as e: messagebox.showerror("CSV Error", f"Failed to read CSV file: {e}") def exit_app(self): if messagebox.askyesno("Exit", "Are you sure you want to exit?"): if self.printer_initialized: try: self.printer.sleep() self.printer.wake() self.printer.setDefault() self.printer.offline() # 将打印机设置为离线状态 self.printer.close() # 关闭串口连接 except Exception as e: print(f"Error during printer shutdown: {e}") finally: self.printer_initialized = False # 重置初始化标志 self.printer = None # 清除打印机对象引用 self.window.destroy() # 关闭打印机窗口 # 函数定义 def new_bean_profile(): global is_running, serial_port, data, last_data_time, is_recording if is_running: is_running = False is_recording = False if serial_port: serial_port.close() start_stop_button.config(text="Start") record_button.config(text="Record", state="disabled") data.clear() last_data_time = 0 table.delete(*table.get_children()) notes_text.delete("1.0", tk.END) initialize_plot() def toggle_recording(): global is_recording if not is_recording: record_button.config(text="Recording...", state="disabled") root.after(2000, start_recording) else: is_recording = False record_button.config(text="Record", state="normal") def start_recording(): global is_recording, last_data_time, data is_recording = True last_data_time = 0 record_button.config(state="normal") data.clear() table.delete(*table.get_children()) initialize_plot() def serial_read_thread(): global is_running, last_data_time, data while is_running: if serial_port and serial_port.is_open: try: line = serial_port.readline().decode('utf-8').strip() if line: parts = line.split(",") if len(parts) == 2: temperature = float(parts[0]) timestamp_ms = int(parts[1]) current_time = time.time() if is_recording and (current_time - last_data_time >= 10): minutes = (timestamp_ms // 60) % 60 seconds = (timestamp_ms // 1) % 60 timestamp = f"{minutes:02}:{seconds:02}" data.append((timestamp, temperature, "")) root.after(0, update_table, timestamp, temperature, "") root.after(0, update_plot) last_data_time = current_time except Exception as e: print(f"读取错误: {e}") def toggle_data_reception(): global is_running, serial_port, data, last_data_time, is_recording if is_running: is_running = False is_recording = False start_stop_button.config(text="Start") record_button.config(text="Record", state="disabled") if serial_port: serial_port.close() else: data.clear() last_data_time = 0 table.delete(*table.get_children()) notes_text.delete("1.0", tk.END) initialize_plot() port = port_combobox.get() baudrate = int(baudrate_combobox.get()) try: serial_port = serial.Serial(port, baudrate, timeout=1) is_running = True start_stop_button.config(text="Stop") record_button.config(text="Record", state="normal") threading.Thread(target=serial_read_thread, daemon=True).start() except Exception as e: messagebox.showerror("Error", f"Failed to open serial port: {e}") def update_table(timestamp, temperature, key_point=""): table.insert("", "end", values=(timestamp, f"{temperature:.2f}", key_point)) table.yview_moveto(1) def update_plot(): ax.clear() ax.set_xlabel("Time (MM:SS)") ax.set_ylabel("Temperature (°C)") ax.set_title("Temperature-Time Curve") if data: timestamps = [d[0] for d in data] temperatures = [d[1] for d in data] key_points = [d[2] for d in data] ax.plot(timestamps, temperatures, 'b-') for i, key_point in enumerate(key_points): if key_point: ax.plot(timestamps[i], temperatures[i], 'ro') ax.annotate(key_point, (timestamps[i], temperatures[i]), textcoords="offset points", xytext=(0,10), ha='center') plt.xticks(rotation=45) plt.tight_layout() canvas.draw() def export_to_csv(): if not data: messagebox.showwarning("Warning", "No data to export") return file_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(defaultextension=".csv", filetypes=[("CSV Files", "*.csv")]) if file_path: try: with open(file_path, mode="w", newline="", encoding='utf-8') as file: writer = csv.writer(file) writer.writerow(["Notes"]) writer.writerow([notes_text.get("1.0", tk.END).strip()]) writer.writerow([]) writer.writerow(["Time (MM:SS)", "Temperature (°C)", "Key Point"]) writer.writerows(data) messagebox.showinfo("Success", f"Data exported to {file_path}") except Exception as e: messagebox.showerror("Error", f"Failed to export data: {e}") def load_csv_file(): file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(defaultextension=".csv", filetypes=[("CSV Files", "*.csv")]) if file_path: try: global data data.clear() table.delete(*table.get_children()) with open(file_path, mode="r", encoding='utf-8') as file: csv_reader = csv.reader(file) next(csv_reader) notes = next(csv_reader)[0] next(csv_reader) next(csv_reader) for row in csv_reader: if len(row) >= 3: timestamp, temperature, key_point = row data.append((timestamp, float(temperature), key_point)) update_table(timestamp, float(temperature), key_point) notes_text.delete("1.0", tk.END) notes_text.insert("1.0", notes) update_plot() messagebox.showinfo("Success", "Data loaded successfully") except Exception as e: messagebox.showerror("Error", f"Failed to load CSV file: {e}") #将 Notes 区域的内容添加到图形中 def export_plot(): if not data: messagebox.showwarning("Warning", "No data to export") return file_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(defaultextension=".png", filetypes=[("PNG Files", "*.png")]) if file_path: # 获取 Notes 的内容 notes = notes_text.get("1.0", tk.END).strip() # 清除之前的图形内容 ax.clear() # 重新绘制温度曲线 timestamps = [d[0] for d in data] temperatures = [d[1] for d in data] key_points = [d[2] for d in data] ax.plot(timestamps, temperatures, 'b-') # 绘制关键点 for i, key_point in enumerate(key_points): if key_point: ax.plot(timestamps[i], temperatures[i], 'ro') ax.annotate(key_point, (timestamps[i], temperatures[i]), textcoords="offset points", xytext=(0,10), ha='center') ax.set_xlabel("Time (MM:SS)") ax.set_ylabel("Temperature (°C)") ax.set_title("Temperature-Time Curve") plt.xticks(rotation=45) # 如果有 Notes 内容,添加到图形的左上角 if notes: ax.text(0.02, 0.98, notes, transform=ax.transAxes, verticalalignment='top', horizontalalignment='left', fontsize=8, bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='white', alpha=0.8)) # 调整布局以确保所有元素可见 plt.tight_layout() # 保存图形 fig.savefig(file_path, bbox_inches='tight') # 更新显示 canvas.draw() messagebox.showinfo("Success", f"Plot exported to {file_path}") def exit_program(): if serial_port and serial_port.is_open: serial_port.close() root.quit() def mark_key_point(event): selected_item = table.selection() if selected_item: menu.post(event.x_root, event.y_root) def mark_return_point(): update_key_point("Return Point") def mark_first_crack(): update_key_point("First Crack") def mark_bean_drop(): update_key_point("Bean Drop") def update_key_point(key_point): selected_item = table.selection() if selected_item: item_data = table.item(selected_item, "values") timestamp, temperature, _ = item_data table.item(selected_item, values=(timestamp, temperature, key_point)) for i, row in enumerate(data): if row[0] == timestamp and abs(row[1] - float(temperature)) < 0.001: data[i] = (timestamp, float(temperature), key_point) break update_plot() def initialize_plot(): global fig, ax, canvas plt.close(fig) fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6)) ax.set_xlabel("Time (MM:SS)") ax.set_ylabel("Temperature (°C)") ax.set_title("Temperature-Time Curve") canvas.get_tk_widget().pack_forget() canvas = FigureCanvasTkAgg(fig, master=plot_frame) canvas.draw() canvas.get_tk_widget().pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True) def copy_selected_data(event): selected_items = table.selection() if not selected_items: return copied_data = [] for item in selected_items: values = table.item(item, 'values') copied_data.append('\t'.join(str(v) for v in values)) copied_text = '\n'.join(copied_data) root.clipboard_clear() root.clipboard_append(copied_text) root.update() # 确保复制到剪贴板 #def open_printer_window(): # PrinterApp(root) def open_printer_window(): printer_app = PrinterApp(root) root.printer_app = printer_app # 保持对打印机应用的引用 # 创建主窗口 root = tk.Tk() root.title("Temperature Monitor") root.geometry("1400x800") # 顶部框架 top_frame = ttk.Frame(root) top_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, padx=10, pady=5) # 串口设置 port_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(top_frame, text="Serial Port Configuration") port_frame.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.X, padx=5, expand=True) ttk.Label(port_frame, text="Port:").grid(row=0, column=0, padx=5, pady=5) port_combobox = ttk.Combobox(port_frame, values=[port.device for port in serial.tools.list_ports.comports()]) port_combobox.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=5, pady=5) port_combobox.set("COM9") ttk.Label(port_frame, text="Baudrate:").grid(row=0, column=2, padx=5, pady=5) baudrate_combobox = ttk.Combobox(port_frame, values=["9600", "115200", "57600", "38400", "19200"]) baudrate_combobox.grid(row=0, column=3, padx=5, pady=5) baudrate_combobox.set("115200") # 控制按钮 control_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(top_frame, text="Control") control_frame.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, fill=tk.X, padx=5) new_profile_button = ttk.Button(control_frame, text="New BeanProfile", command=new_bean_profile) new_profile_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5, pady=5) start_stop_button = ttk.Button(control_frame, text="Start", command=toggle_data_reception) start_stop_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5, pady=5) record_button = ttk.Button(control_frame, text="Record", command=toggle_recording, state="disabled") record_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5, pady=5) load_csv_button = ttk.Button(control_frame, text="Load CSV", command=load_csv_file) load_csv_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5, pady=5) export_csv_button = ttk.Button(control_frame, text="Export CSV", command=export_to_csv) export_csv_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5, pady=5) export_plot_button = ttk.Button(control_frame, text="Export Plot", command=export_plot) export_plot_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5, pady=5) printer_button = ttk.Button(control_frame, text="Printer", command=open_printer_window) printer_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5, pady=5) exit_button = ttk.Button(control_frame, text="Exit", command=exit_program) exit_button.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5, pady=5) # 中间框架 middle_frame = ttk.Frame(root) middle_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=10, pady=5) # 左侧数据表格 table_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(middle_frame, text="Data Table") table_frame.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=5, pady=5) columns = ("Time (MM:SS)", "Temperature (°C)", "Key Point") #table = ttk.Treeview(table_frame, columns=columns, show="headings", height=10) table = ttk.Treeview(table_frame, columns=columns, show="headings", height=10, selectmode='extended') table.heading("Time (MM:SS)", text="Time (MM:SS)") table.heading("Temperature (°C)", text="Temperature (°C)") table.heading("Key Point", text="Key Point") table.pack(side=tk.LEFT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True) scrollbar = ttk.Scrollbar(table_frame, orient="vertical", command=table.yview) scrollbar.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, fill=tk.Y) table.configure(yscrollcommand=scrollbar.set) # 右侧标签区域 right_label_frame = ttk.Frame(middle_frame) right_label_frame.pack(side=tk.RIGHT, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=5, pady=5) # 上方自定义标签 custom_label_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(right_label_frame, text="Custom Label") custom_label_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=5, pady=5) custom_label = tk.Text(custom_label_frame, wrap=tk.WORD, height=5) custom_label.insert(tk.END, "2025-MM-DD HH:MM\nCoffee varieties:\nelevation:\nkey point:") custom_label.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=5, pady=5) # 下方Notes区域 notes_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(right_label_frame, text="Notes") notes_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=5, pady=5) notes_text = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(notes_frame, wrap=tk.WORD, height=5) notes_text.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=5, pady=5) # 底部图表面板 plot_frame = ttk.LabelFrame(root, text="Temperature-Time Curve") plot_frame.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True, padx=10, pady=5) fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6)) canvas = FigureCanvasTkAgg(fig, master=plot_frame) canvas.get_tk_widget().pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True) # 在这里初始化图形 initialize_plot() # 添加右键菜单 menu = tk.Menu(root, tearoff=0) menu.add_command(label="Mark as Return Point", command=mark_return_point) menu.add_command(label="Mark as First Crack", command=mark_first_crack) menu.add_command(label="Mark as Bean Drop", command=mark_bean_drop) # 绑定右键点击事件 table.bind("<Button-3>", mark_key_point) # 绑定Ctrl+C快捷键到表格 table.bind('<Control-c>', copy_selected_data) # 启动主循环 root.mainloop()IV. Hardware List Used
4.1 PART A: Front-end Acquisition and Transmission Terminal
(1) Platinum RTD Temperature Sensor: PT100
(2) Temperature Sensor Amplifier: MAX31865
(3) Main Control Module: M5Stack AtomS3. Programming uses VSCode + PlatformIO + Arduino framework.
(4) Connecting wires and 3D printed enclosure.4.2 PART B: Roasting Glasses
(1) Main Control Module: M5Stack AtomS3, UI design.
(2) Power Management Module: 200mAh lithium battery and its charging management module, micro switch.
(3) Optical Components: Magnifying lens, mirror, beam splitter prism.
(4) 3D printed structure for the glasses.
(5) A pair of transparent safety goggles, used to mount the roasting glasses structure.4.3 PART C: PC Monitoring and Printing
(1) Thermal Printer: 58MM, communicates with PC software via TTL level.
(2) USB-TTL converter module.
(3) A PC with a Python environment and necessary libraries installed.V. What Makes Your Project Special
- Very Interesting: This is a glasses-style smart wearable device providing a semi-transparent display. The player can view real-time data through the beam splitter prism of the glasses while roasting coffee beans, without interfering with the observation and operation of the coffee roasting process. Both hands remain free for normal roasting operations.
- Very Lightweight and Sturdy: Uses 2 M5Stack AtomS3 modules, making the structure very compact, especially the glasses part. It fully utilizes the high integration of the M5Stack AtomS3 module. The bright screen provides sufficient light for the glasses; after reflection, magnification, and beam splitting, the user can observe the data very clearly. Mounted on a pair of transparent safety goggles, it's convenient and stable to wear, very lightweight (only ** grams including the goggles and glasses assembly), and does not feel burdensome.
- Very Reliable: Uses the ESP-NOW wireless protocol. The two M5Stack AtomS3 modules handle data acquisition/transmission and reception/display respectively. No WiFi router/access point is needed, meeting real-time transmission requirements. The transmission is reliable and simple.
- Very Practical: This is a practical wearable device. I have already used it to assist in roasting over 2000g of coffee beans. It's particularly helpful for grasping the temperature rise rate and roasting time. I've also fully experienced the distinct differences between Ethiopian natural/washed beans and Panamanian mountain beans through the data. Understanding the roasting process through data is very interesting and practical. It has already become a useful little electronic device in my kitchen.
- Reproducible: I will open-source all the code, wiring diagrams, and 3D print files, hoping more coffee enthusiasts can try this interesting device.